National Planning Framework
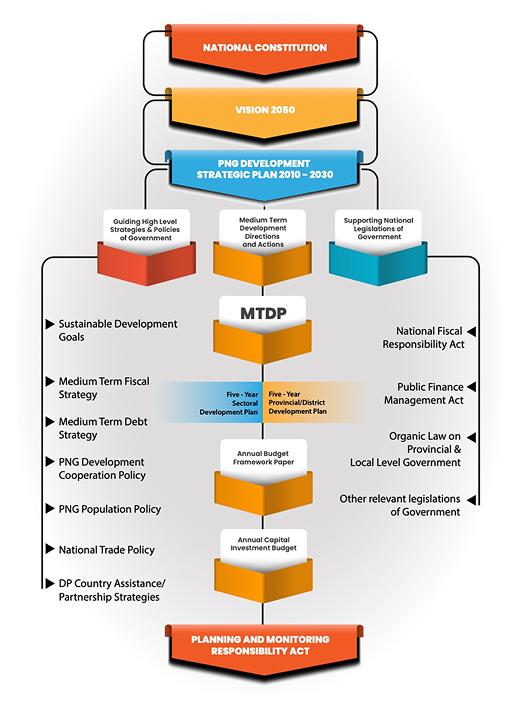
The *Planning and Monitoring Responsibility Act (PMRA) 2016* helps guide the country’s growth and development by setting up five important frameworks, or plans, to make sure all efforts are well-organized. Here’s a simple breakdown:
- *National Planning Framework* – This is like a master plan for the country’s development, showing what needs to be done to grow the economy and improve people’s lives.
- *National Budget Framework* –This ensures that money is spent wisely and on the right projects to support the country’s development goals.
- *National Service Delivery Framework* – This focuses on getting essential services (like healthcare, education, and infrastructure) to the people who need them.
- *Monitoring and Evaluation Framework* – This checks if development projects are working well and meeting their goals, helping to fix issues along the way
- *Development Cooperation Partnership Framework* – This encourages teamwork with partners, like other countries and organizations, to help the country achieve its long-term plans.
Together, these frameworks ensure the country’s plans are well-coordinated, progress is tracked, and resources are used efficiently to improve people’s lives.
Monitoring and Evaluation Framework
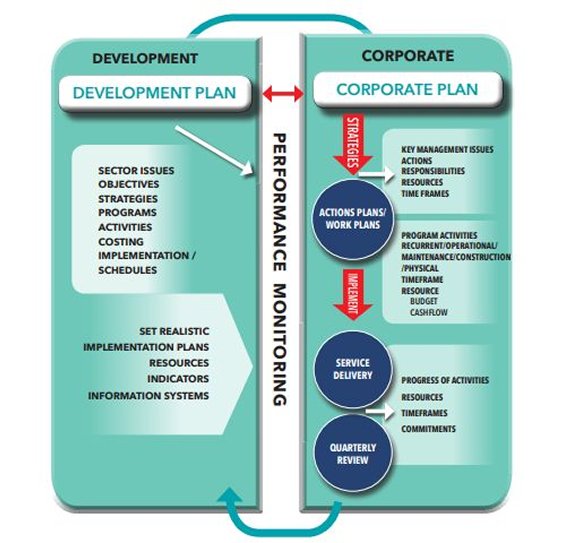
The National Policy Monitoring and Evaluation Framework (PMEF) sets out the basic concepts, principles, and approaches for monitoring, evaluating, and reporting the performance and results of national policies, plans, and strategies in Papua New Guinea (PNG).
Framework aims to promote performance, accountability, and enhance effectiveness of public policies and services in our country. The strategic benefits of implementing this Framework will allow the Government to:
- Make prudent use of our limited resources; people’s lives.
- Address rising expectations from ordinary citizens that the Government should provide more services at a higher quality;
- Support accountability pressures from the Parliament that Government should publicly report and explain their performance;
- Meet increasing demand of development partners in measuring and managing for results.
National Service Delivery Framework
The National Service Delivery Framework (NSDF) sets out the minimum level of services that the National, Provincial, District and Local Level Governments will provide at each designated services delivery center.
The NSDF provides a guide for the national government, Provincial Governments, Local Level Governments and District Development Authorities and the agencies and institutions of government to work in partnership with each other to better integrate frontline service delivery settings and improve quality of life for all Papua New Guineans.
Frontline service delivery in Papua New Guinea is critical because most of our people live in rural areas and access is limited due to inadequate enabling infrastructures like transport and amenities to enable timely availability of services for the people.
Together, these frameworks ensure the country’s plans are well-coordinated, progress is tracked, and resources are used efficiently to improve people’s lives.
Our vision for Frontline service delivery in PNG:
improving access to quality service to all Papua New Guineans, in particular those in rural areas of PNG;
Provide real time service; Access all year around;
Continuous improvement and customer satisfaction;
Service User or customer contribution in co-production of services suited to their unique needs.
Annual Budget Framework Paper
The Annual Budget Framework Paper (ABFP) is a strategic document that links the National Planning Framework, Medium-Term Development Plan (MTDP) and the expenditure priorities of the Capital Investment Budget each year, and serves as an input to the Budget Strategy Paper (BSP)
Section 6 of the Papua New Guinea (PNG) Planning and Monitoring Responsibility Act, 2016 (the Planning Act) warrants the production of the Annual Budget Framework Paper (ABFP) annually and guides the formulation of the Capital Investment Budget.
It is published four (4) months before the tabling of National Budget in Parliament. The ABFP reconciles the Government’s policy priorities (“development needs”) with the fiscal envelope (“availability of funds”) and guides the selection of investments, in alignment with the Government’s Development Priorities and Aspirations, funded through the capital component of the National Budget.
The ABFP also provides the trend of expenditures in the Capital Investment Budget and sets sectoral ceilings and guides sectoral priorities for the forward year. Sectoral consultations are undertaken to determine the priorities within the sector and against the set ceilings.